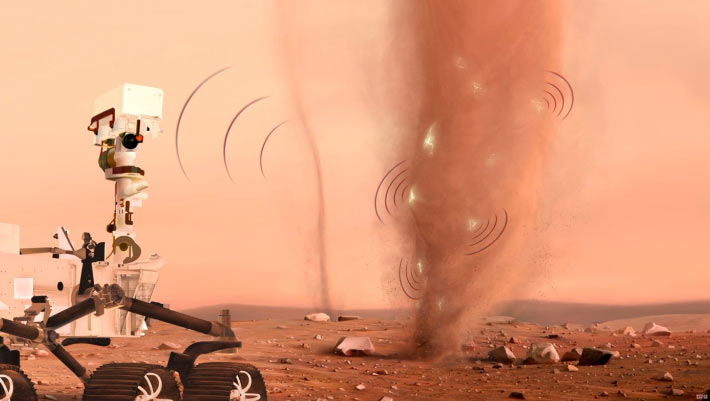
Planetary scientists have cataloged 55 instances of triboelectric discharge events, linked to Martian dust devils and dust storms, by analyzing data acquired by the SuperCam microphone aboard NASA’s Perseverance rover over a two-year Martian period.

Detection of electric discharges in dust devils by the SuperCam instrument on board NASA’s Perseverance rover on Mars. Image credit: Nicolas Sarter.
Within our Solar System, electrical phenomena such as lightning are observed on Earth, Saturn, and Jupiter.
While the presence of electrical activity on Mars has been posited, it had not been empirically confirmed until now.
The arid Martian surface is frequently characterized by a spectrum of transient and widespread phenomena, including aeolian dust and sand transport, dust events, and dust whirlwinds, all of which are known contributors to electrification on Earth.
Elucidating whether such electrification occurs on the Red Planet is paramount, as it significantly enhances our comprehension of the planet’s surface chemistry and could have implications for the operational safety of both robotic and future human expeditions.
In pursuit of this objective, Baptiste Chide, a researcher at Université de Toulouse, along with his team, meticulously examined 28 hours of audio recordings captured by Perseverance’s SuperCam microphone across two Martian years precisely.
By discerning acoustic signatures and interference patterns characteristic of electrical discharges, the researchers identified and classified 55 distinct electrical events.
Their analysis revealed that approximately 54 of these events coincided with the upper 30% of the most intense wind conditions recorded throughout the investigation, underscoring the pivotal role of wind in initiating electrical charge accumulation on Mars.
Furthermore, sixteen of these events were documented during the rover’s sole two close encounters with dust devils, suggesting the potential for more numerous, albeit weaker or more distant, discharges to have occurred beyond the microphone’s detection threshold.
These findings strongly indicate that the Martian atmosphere exhibits electrical dynamism, particularly during localized dust-lifting events rather than during periods of global dust saturation.
“On Earth, atmospheric electricity is primarily driven by the accumulation of electrical charge within clouds and storms, leading to violent discharges in the form of lightning,” explained Dr. Ricardo Hueso, an investigator at the University of the Basque Country.
“In contrast, atmospheric electricity on Mars is a dry phenomenon, generated by the friction and collisions between dust particles within whirlwinds and dust storms, resulting in considerably less energetic discharges compared to terrestrial lightning.”
“Mars, with its tenuous carbon dioxide atmosphere, presents a cold, arid, and dusty environment where powerful winds, often manifesting as gusts and generating whirlwinds and rising dust plumes, are prevalent,” elaborated Dr. Agustín Sánchez-Lavega, also affiliated with the University of the Basque Country.
“This can lead to the formation of vast storm fronts extending for hundreds of kilometers, occasionally enveloping the entire planet in a shroud of dust.”
“Consequently, we anticipate that the previously undetected electrical discharges would be exceptionally frequent under these prevailing environmental conditions.”
“Our research initiates a new avenue of inquiry into the multifaceted effects of natural electrical phenomena on the Martian atmosphere,” the researchers concluded in their report.
Their comprehensive publication was officially released on November 26, 2025, within the esteemed journal Nature.
_____
B. Chide et al. 2025. Detection of triboelectric discharges during dust events on Mars. Nature 647, 865-869; doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-09736-y