The newly unveiled map and digital repository, christened Itiner-e, substantially augment the cataloged extent of the Roman Empire’s transportation infrastructure, adding over 110,000 kilometers.
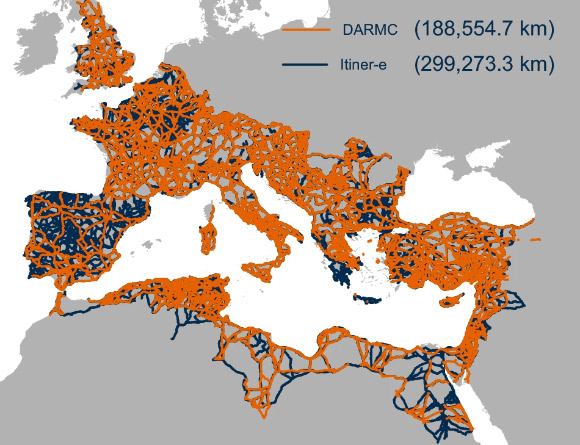
Itiner-e stands as the most granular and exhaustive publicly accessible digital inventory of thoroughfares within the Roman Empire’s dominion. Image attribution: de Soto et al., doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-06140-z.
During its zenith in the second century Common Era, the Roman Empire encompassed a populace exceeding 55 million individuals and spanned territories from present-day Britain to Syria and Egypt.
While a sophisticated network of roadways was instrumental in the Empire’s expansion and consolidation, its complete cartographic representation remains elusive, and existing digital renderings possess a limited degree of detail.
“The scholarly investigation into the Roman Empire’s road systems has been a persistent pursuit for centuries,” remarked Tom Brughmans, a researcher from Aarhus University, alongside his collaborators.
“A vast repository of information exists concerning routes physically identified through archaeological excavations and surveys; on milestones strategically positioned at regular intervals along Roman thoroughfares; and in historical accounts such as the Antonine Itinerary or the Tabula Peutingeriana, which delineate principal conduits between settlements, as well as providing intricate regional summaries of Roman roadways.”
“Nevertheless, the collation and pinpointing of this diverse body of research, alongside the spatially precise determinations of the road segments themselves, are hindered by a deficiency in any overarching synthesis and digitization efforts across the entire Empire.”
The research team meticulously compiled Itiner-e, drawing upon archaeological findings, historical documentation, topographical charts, and satellite imagery.
The resultant dataset encompasses 299,171 kilometers of roads, representing an increment from the prior estimation of 188,555 kilometers, and covers an area of nearly 4 million square kilometers.
The investigators posit that this expanded coverage is attributable to more thorough mapping of roads in regions such as the Iberian Peninsula, Greece, and North Africa, as well as the recalibration of previously posited routes to align with geographical realities.
This recalibration includes the accommodation of roads traversing mountainous terrain, allowing them to follow sinuous trajectories rather than adhering to purely linear paths.
Itiner-e is structured to include 14,769 distinct road segments, of which 103,478 kilometers (constituting 34.6%) are categorized as primary routes, and 195,693 kilometers (65.4%) are designated as secondary routes.
The exact geographical coordinates for merely 2.7% of these roads are definitively established, while an additional 89.8% are known with less precision, and 7.4% remain hypothetical.
“Itiner-e stands as the most detailed and comprehensive publicly accessible digital rendition of the Roman Empire’s road network, concurrently illuminating the existing lacunae in our contemporary understanding of this infrastructure,” stated the authors.
“They further observed that Itiner-e is incapable of illustrating temporal shifts within the road system, and that forthcoming investigations are imperative to explore this aspect comprehensively throughout the Roman Empire.”
“The Itiner-e resource holds considerable potential for future scholarly endeavors aimed at examining the impact of Roman roads on connectivity, governance, population movements, and the propagation of diseases within the Empire’s vast territories.”
The cartographic representation and associated dataset have been documented in a publication featured in the esteemed journal Scientific Data.
_____
P. de Soto et al. 2025. Itiner-e: A high-resolution dataset of roads of the Roman Empire. Sci Data 12, 1731; doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-06140-z